Efficient Manufacturing and the Eight Wastes#
Lean manufacturing, also called lean production, is an approach to manufacturing with several goals.
- Eliminate as much waste and idle time as possible
- Deliver output at a cost consistent with the design level of quality
- Produce products that compete well in the market
Eight Wastes#
- Transportation/Logistics
- Inventory
- Motion
- Waiting
- Over Processing
- Over Production (Worst waste!!)
- Defects
- Human Resources
Efficient Supply Chain Processes#
Several operational characteristics define a lean supply chain and differentiate it from those procurement systems that have failed to create lean processes.
Fewer Vendors and Less Staff#
In many manufacturing processes, several vendors are used to supply the same part. The logic here is that each one will complete the order to provide the lowest cost at the highest quality. This is creates competitive environments among the vendors. But in a lean environment, creating a competitive environment is given much less emphasis. In fact it is not unusual to find that only one supplier is chosen. Rather than an arms length relationship with multipe suppliers, a closer partnership is created with a single supplier.
One consequence of using fuel suppliers is that much smaller procurement staff it is needed. So fewer suppliers and smaller staff contribute to as much leaner supply chain system
Relationship with Suppliers#
When few vendors are used. It now becomes necessary to build a closer relationship with those that remain. it is particularly true of those standard that surprise critical components to the manufacturing plants. Often those vendors referred to as a strategic suppliers. There’s a difference between suppliers, some some vendor supplying critical components, while some other vendor only supplying commodity parts, and the relationship with them would be much less formal.
Contracts and Prices#
In a traditional supply chain relationship contract may only covers the current order, but in lean supply chain, it is more common to find longer contracts that extent over several order cycles. Similarly, in conventional relationships, pricing is a competitive process and one party gains is seen as the other party’s loss. So it is seen by both sides as an adversarial process
But in lean relationships, both parties work together agree on pricing targets, and work towards common goals. As a result, price changes, accessory price increase a less likely to occurred overtime both books together to reduce them through development of better tech, technologies and more efficient processes. Why?
They both understand the need to contain course and price in the interest of protecting growing the host’s companies market share.
Quality#
Quality control is the most traditionally manage supply chain system depend heavily on the quality control standards and incoming inspection systems used by the host company. But quality control in lean system is very different, standard and inspection system extend across the host and vendor organization, so it is the responsibility of both to deliver the right product at the right price and at the desired qualtiy level. Quality is now a joint concern of the strategic partnership.
Inventory#
Because fewer suppliers are used, and the relationship with these suppliers is closer, it is possible to implement a system call JIT, where small shipments are delivered as they are needed by the host company. This goes a long way in eliminating the need for large inventory levels to act as buffer from sudden fluctuations in supply. The responsibility for a timely arrival of goods and services now reside with stratgic suppliers.
Production Flexibility#
The origanization and its vendors must maintain enough flexibility to make the more permanent process or design changes to maintain their competitive position.
Communication and Information Flow#
In the non lean environment, communication between the firm and its suppliers is limited but this changes significantly in lean system. As a result, communication increases as both parties work to coordinate their efforts as partner rather than adversaries.
Efficient Product Development Processs#
Fist to Market:#
Speeding a product though the pipeline has many advantages. One is to increase the chances that if you’ll be first to market, an expressions referring to the situations where a new product is introduced into the marketplace her head of competition.
The company that is the first to market enjoy the advantage and securing market share. So first to market matters!
Characteristic of lean product development#
Lean product developments, differ from continuous process in several important ways
- Treated as projects
- Emphasis on innovation and knowledge
- Focusing on marketplace
- Lean emphasis on manufacturing
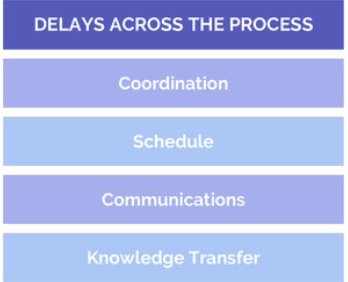
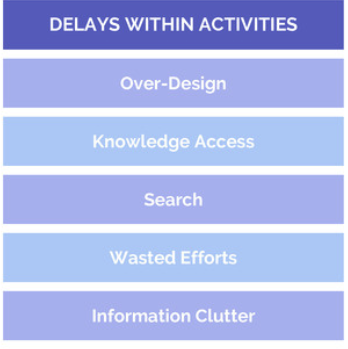
The Challenges of Six Sigma#
Problem Finding#
The problem finding process is central to the Lean 6 Sigma process. It is also a major challenge because no problem can be solved until its source is found.
Managing Process Mean and Variation#
The second challenge is monitoring and controlling an operational process to ensure that it is operating as expected. These processes can be monitored and controlled using two parameters: mean and variation.
Six Sigma Tools#
Control Charts#
A control chart adds three dimensions to the line chart. At the center of the chart is a target level. It represents the average output from a process that is stable and in control. Sample means are expected to vary on both side of the target since no process can be perfectly consistent.
If the sample means for customer satisfaction, fell below the LCL in any month, management would consider that the process is no longer in control. It would suggest that the mean output had shifted and that the entire service process was no longer delivering the customer value it had previously delivered. In other words, the process would now be considered out of control.
The horizontal line above the target is call Upper Control Limit (UCL). It represents the point above, in which sample mean results suggest that the process is out of control and that the mean output from the process is no longer meeting expectations.
Once effective processes have been designed and once appropriate statistical control charts have been implemented, the goal is to maintain the stablity of the process. We would expect sample means to fall within the LCL and UCL.